New Discovery Gives Hope to People With High Chances of Antibiotic Resistance
There is new hope for roughly 700,000 individuals who die each day due to antibiotic-resistant inflammations. Recently, researchers from the University of Queensland discovered how bacteria, particularly "superbugs," are contributing to antibacterial-genes.
According to Professor Mark Schembri from UQ, the antibiotic-resistant bacteria, particularly the emerging superbugs, could cause the death of roughly 10 million people all over the world by 2050.
Professor Schembri added that the lessening pool of efficient antibiotics is making such inflammations a major risk to public health. Thus it is crucial that we understand the precise procedures of how antibiotic resistance is spreading between various bacteria.
In the study, researchers devised plasmids—DNA molecules that are self-replicating. They are also among the major drivers for the quick transmission of antibiotic resistance genes between one bacteria cell to another.
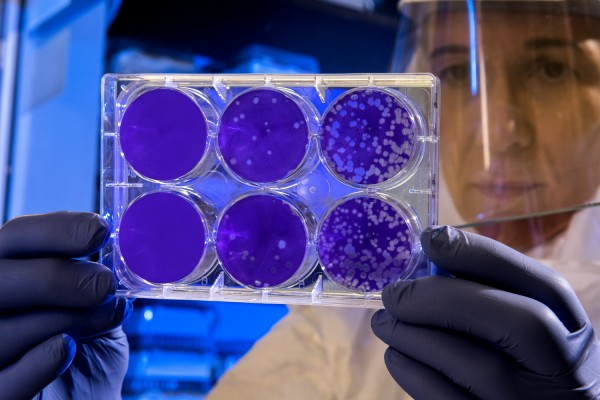
Researchers from the University of Queensland are seeing common infections resulting from ‘superbugs, resistant to all existing antibiotics, accenting the increasing struggle of antibiotic resistance.
ALSO READ: A New Research Finding Says Parasite in the Brain Is Not Making One Sick
How Plasmids Self-Replicate
According to the study authors, a lot of plasmids carry around 10 to 15 antibiotic resistance-causing genes. And the moment they get transmitted from one bacteria cell to another, two essential occurrences take place.
First, as indicated in the research, the plasmid copied to it gets retained both by the recipient and donor cells. Second, all antibiotic resistances are transmitted together, which means resistance to multiple antibiotics can be transmitted and, at the same time, acquired.
Dr. Steven Hancock, the study's lead author, used a potent inherent screening system to determine all components needed for the transmission of an essential antibiotic resistance placid type from a single bacterial cell to another.
Dr. Hancock added that they found genes encoding the 'syringe' component. This is the procedure where mobilization of plasmid DNA is carried out, while involving an innovative regulatory component vital for the control of the transmission process.
DON'T MISS THIS: Rare Condition: Teeth in Brain Tumor, Here's What Medicine Explains
Reduction of Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes
The study authors also examined the crystal construction of the said controling component and found how it binds to DNA and stimulates transcription of other genes engaged in transmission.
Professor Schembri also explained that this deeper knowledge would open the door to solve this constantly growing health problem.
The professor also said that preempting the transmission of plasmids between bacteria has been a big problem in the reduction of the spread of antibiotic resistance genes.
Effective Solution Needed
By observing the molecular procedures, Dr. Schembri said, "We can begin developing effective solutions" to stop the said genes in their tracks.
Nearly all people have experienced such an inflammation that failed to immediately respond to the initial treatment round through the use of antibiotics, only to be lucky enough to undergo a treatment with much more effective antibiotics.
In life-threatening cases, we see common infections resulting from superbugs resistant to all existing antibiotics, accenting the increasing struggle of antibiotic resistance.
It is also essential to address this issue now; the professor is eager to see how this new and deeper understanding will result in novel methods, possibly saving millions of lives worldwide.
Nature Microbiology recently published the said research made by Dr. Schembri and his team.
IN CASE YOU MISSED IT: Case Report at Children's National Hospital Raises Concern for Resistance to Antibiotic
Check out more news and information on Immunity on MD News Daily.
Aug 18, 2020 12:12 AM EDT