Rare Condition: Teeth in Brain Tumor, Here’s What Medicine Explains
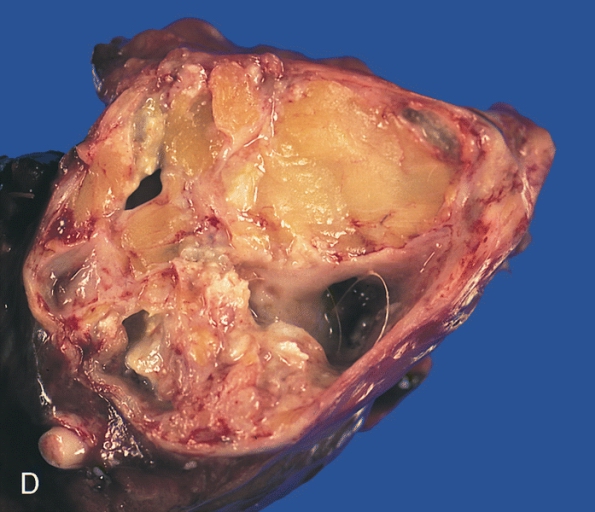
A horizontal slice of the resected tumor reveals fibrofatty tissue, calcified areas, and a few cystic spaces lined with a smooth membrane and containing a hair.
In 2014, a four-month-old baby in Maryland was reported to have been the first person to have teeth "form" in his brain, resulting from a particular type of brain tumor.
The case report said that the boy is now doing well with his tumor removed. But during that time, the doctors said that the baby's condition shed light on how rare tumors like this developed.
At first, the doctors reportedly suspected something was not right when the boy's head seemed to have grown faster than how it usually did for other kids his age.
A brain scan showed that a tumor that had structures looking "very similar to teeth" typically found in the lower jaw.
Following the finding, the child went through a brain operation so that the tumor would be removed. The said report also said that it was during the surgery when the doctors discovered that the said lump contained a few fully formed teeth.
ALSO READ: Study Shows How Pickled Capers Can Benefit the Heart and Brain
Doctors' Finding
Doctors were able to identify that the child had a craniopharyngioma. This is a rare tumor in the brain that could grow larger than a golf ball, although it does not spread.
Typically, craniopharyngiomas have calcium deposits. In the boy's case though, the doctors said when they pulled a full tooth out, they thought it was a condition that was slightly different.
According to the University of Maryland Medical Center's Dr. Narlin Beaty, teeth have been discovered in the brains of people.
However, the doctor added, "only tumors known as 'teratomas' which are distinctive among the other tumors" as they consist of three of the types of tissues found in a human embryo at its early stages. On the contrary, craniopharyngiomas contain just a single layer of tissue.
DON'T MISS THIS: Could Sudoku Puzzles Cause Seizures? A Look at Intense 3D Imagination
Who are Likely to Have Teratoma?
Teratoma is a rare tumor type that can have fully-grown tissues and organs which include hair, teeth, bone, and muscle.
Specifically, this type of tumor commonly appears in ovaries, tailbone, and testicles. Nevertheless, it can take place elsewhere too, in any part of the body.
Medical reports state that teratomas choose no age. They can occur in infants, children, or even adults. Additionally, they are typical in females.
Meanwhile, a teratoma, when taking place in infants, is commonly benign although it may need to be surgically removed.
Teratoma Types
Medical experts classify teratomas as either mature or immature. Mature teratomas, or dermoid cysts, are typically not cancerous or benign. However, mature teratomas may develop again after they are removed through surgery.
Immature teratomas are more possible to grow into malignant cancer. Further classifications of mature teratomas include cystic, solid, and mixed.
Common Symptoms
Initially, teratomas may not show any symptoms, which vary according to the area where the teratoma is located.
The most typical locations for this type of tumor are the tailbone or coccyx, testicles, and ovaries. Other common signs and symptoms of this condition include pain, bleeding and swelling, mildly raised alpha-fetoprotein or AFP levels, and moderately elevated hormone beta-human chorionic gonadotropin or BHCG levels.
Teratomas typically result from complications in the growth process of the body, including how cells differentiate and specialize.
Furthermore, this tumor type arises in the germ cells, which are produced quite early in the fetus's development.
One of the teratoma theories suggests that such a condition originates in the primordial germ cells. The said theory explains how a teratoma is found with wax, hair, or teeth. It can even appear as a nearly-formed fetus.
Treatment
If a teratoma is identified in its fetal stage, the doctor carefully monitors the mother's pregnancy.
If the tumor remains small, normal delivery is typically planned. However, if the teratoma is larger in size, or there is amniotic fluid access, the doctor usually plans for an early or advanced cesarean delivery.
In rare conditions, fetal surgery is required to take out the sacrococcygeal teratoma or SCT before it can lead to possibly fatal complications.
SCTs identified right after birth, are removed through surgery. They need to be monitored very carefully as there is a substantial chance of growing or developing again within the next three years.
Meanwhile, if the teratoma is found to be malignant, the use of chemotherapy together with an operation is usually done. Now, with modern chemotherapy, survival rates for this type of teratoma are high.
IN CASE YOU MISSED IT: A Rare Condition of Brain Fluid Leaking Due to Pilates? Here's What You Need to Know
Aug 01, 2020 08:20 AM EDT