Case Report at Children’s National Hospital Raises Concern for Resistance to Antibiotic
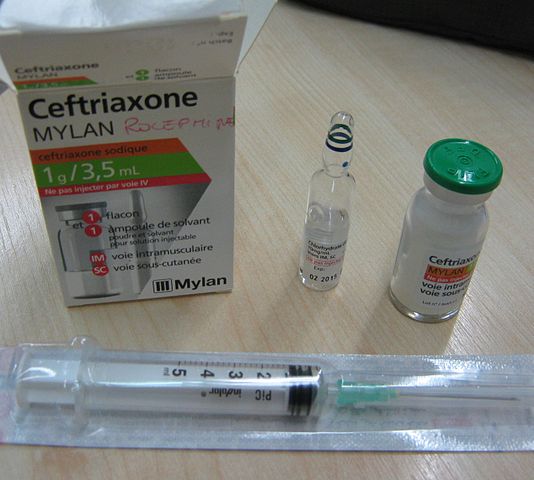
A patient's N. meningiditis infection got cleared after using ceftriaxone for seven consecutive days.
Researchers recently reported a meningitis case at the Children's National Hospital, raising serious concerns about resistance to antibiotics in the common bacterium it resulted from.
The study, which the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Disease Society published earlier today, could change laboratory and clinical practice" throughout the United States and possibly, all over the world.
The said research specified, Neisseria meningitis or N. meningitidis is the leading cause of bacterial meningitis among adolescents. It is a vital root of illness in young children, too.
Gillian Taormina, DO, one of the authors of the case report and a fellow in Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Children's National, and Joseph Campos, Ph.D. and Microbiology Laboratory and the Infectious Diseases Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory Director at Children's National both explained the study:
As standard clinical practice in the country, patients who are suspected of having such an infection are initially treated with the antibiotic ceftriaxone while waiting for a result from the microbiological laboratory to determine the causative organism from either cerebrospinal fluid samples or blood.
Once the bacterium has reportedly been detected to be N. meningitidis, patients usually get treated through administration of ampicillin or penicillin, antibiotics with a smaller range of activity, less possibly to result in resistance to ceftriaxone.
Members of the family and other contacts close to them are frequently prophylactically cured with the administration of an antibiotic, also known as ciprofloxacin.
ALSO READ: Physicians Have Established New Guidelines for this Hard-to-Diagnose Condition
Sensitive to Antibiotics
Since N. meningitidis has been popularly susceptible to the antibiotics mentioned, the majority of the labs are not conducting tests to validate vulnerability to the drug, explained Dr. Campos.
Nonetheless, the practice at Children's National is to screen such isolates for resistance to ampicillin and penicillin through a rapid five-minute test.
Essentially, the isolate from Dr. Taormina's five-month-old patient--a then healthy Maryland-based infant who was brought to the emergency room at the Children's National six days from having fever and congestion--reportedly produced astonishing results.
Specifically, the tests resulted in N. meningitidis developed from the blood of patients, also tested positive for beta-lactamase, an enzyme that damages the active element in the family of antibiotics, including ampicillin and penicillin. Similarly, the isolate was discovered to be resistant to ciprofloxacin.
DON'T MISS THIS: Researchers Identify New Cause of Age-Related Hearing Loss
Ciprofloxacin Resistance
Reports also indicated that when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or CDC, asked other state labs to send their respective samples for N. meningitidis to be tested, 33 samples had positive results for beta-lactamase.
Similar to the bacterium separated from the patient of Dr. Taormina, 11 of them were reportedly ciprofloxacin-resistant.
The said bacteria, Taormina explained, would not have been vulnerable to the usual antibiotics that would not be typically used for such an infection.
Therefore, the doctor added, it is entirely probable that the inflammations, which the bacteria caused, could have been unsuitably treated if doctors employed the standard procedure.
Furthermore, Taormina elaborated that her patient's infection got cleared after seven consecutive days of using ceftriaxone, his originally-prescribed antibiotic.
Family members of the patient and their close contacts were treated prophylactically with rifampin, instead of ciprofloxacin.
A Growing Concern
Even though the said condition had a positive result, Dr. Campos claimed that it raised the alarm for other infections of N. meningitidis in the country, where resistance to antibiotics has turned out to be a growing concern.
IN CASE YOU MISSED THIS: Research Shows Link Between Flu and Pneumonia Vaccines and Alzheimer's Disease
Aug 03, 2020 08:00 AM EDT