Flash Fire Igniting During Surgery: Know How it Happens and How to Prevent It
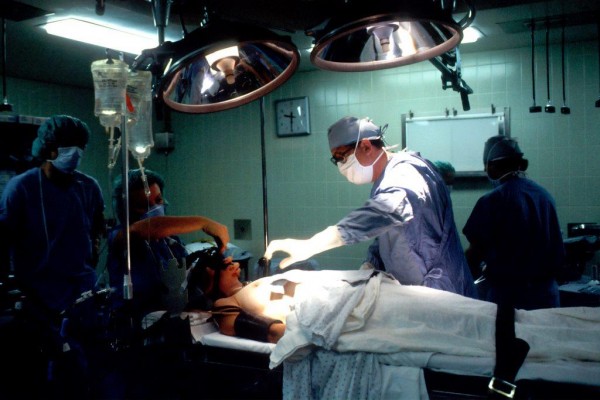
: During the operation, surgeons reportedly used an 'electrocautery device which heats tissue' through electricity to stop the bleeding in the blood vessels.
When one thinks about the dangers of surgery, the term "fire" typically does not come to mind. However, this was what took place when a man in Australia felt a "flash fire" in his chest cavity while he was going through an emergency heart operation.
While fires, while surgery is going on, are rare, not to mention, "Chest activity fires," even more atypical, this particular case, according to Dr. Ruth Shaylor, emphasizes the continuous need for training for fire and preemptive tactics during operation.
In a statement, Shaylor said, doctors, specifically, need to be aware that certain conditions during surgery, which include the presence of high levels of oxygen, along "with sources of heat," can augment the danger of fires.
A Case Reported
In the said new case, there is a need for a 60-year-old male patient to undergo surgery to have a tear in his aortic artery fixed.
The aortic artery is the main artery located in the chest, carrying blood out of the heart. Relatively, the man had formerly been detected with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
During the surgery, surgeons noticed that the right lung of the man was "stuck to his sternum or breastbone." They noticed too that some of the lung tissues had turned out "overinflated."
Such areas, according to the reported case, are also called "bullae" and are frequently results of COPD. Additionally, surgeons, as indicated in the report, tried to evade or circumvent the bullae as they opened the sternum of the patient to access his chest.
However, despite the cautious effort, the doctors reportedly perforated one of the bullae, resulting in an air leak from the lung of the man.
DON'T MISS THIS: Can the Human Body Brew Beer? Here's What You Need to Know About Auto Brewery Syndrome
How the Flash Fire Happened
When the incident transpired, surgeons said they needed to give the patient "higher dose of supplemental oxygen" so they could prevent difficulty in breathing.
Later in operation, surgeons reportedly used an "electrocautery device which heats tissue" through electricity to stop the bleeding in the blood vessels.
Unexpectedly, flashes from the device, as mentioned earlier, kindled a fire on the surgical gauze. The fire was rapidly extinguished with saltwater, without causing injury to the man.
Dr. Shaylor also explained that despite the fire incident, the rest of the surgery turned out well and successful, and surgeons were able to repair the aortic tear successfully.
How a Flash Fire or Surgical Fire Happens
According to research, "flash fire," also called "surgical fire" occurs "in, on or around a person who is undergoing a surgical or medical procedure."
It may take place any time there is the presence of all three components, including fuel sources, ignition source, and oxygen. These three are also called the "fire triangle."
According to medical experts, most people are aware of the level of danger the said elements "combined can be."
More so, surgical fires are considerably underreported, and they take place totally too frequently, leading to adversity for the patient.
Importance of Educating the Entire Medical and Surgical Teams
Recent case reports indicated that the most conventional ignition sources include the electrosurgical equipment at 68 percent and lasers at 13 percent.
In addition, an environment augmented by oxygen can be a contributing factor in more than 70 percent of all surgical fire incidents. In relation to this, each surgical group member controls a particular aspect of the triangle mentioned.
The surgeon, for instance, controls the source of heat while the nurses "control the fuel." The anesthesiologist, on the other hand, has control over the oxidizer.
Health and medical experts explained, if surgical teams are well informed and are aware of the manner of adequately managing the components mentioned, flash sires or surgical fires can be prevented.
And, even though such teams know how to take essential protections, there are still some members of the medical team who are totally not prepared, in too much of a rush, or are uninformed about the real dangers involved.
IN CASE YOU MISSED THIS: Penile Ossification: An Unusual Case Men Should Be Aware Of
Jul 15, 2020 08:30 AM EDT